Difference Between Thunderbolt and USB-C: All Explained
August 14, 2023 9 min read
Understanding the nuanced differences between Thunderbolt and USB-C, as well as their respective docks/hubs, can indeed be challenging. However, by considering factors such as data transfer speed, power delivery options, and minimum linkage speed, I've identify their unique attributes. These standards may overlap in certain areas, but they also diverge significantly in others, further complicated by issues around ports and standardization.
Let's blow away the fog. And slip to the points that demand your focus.
You'll explore how USB and Thunderbolt standards affect your daily life. Even I've hinted how a longer USB-C cable can turn a rabbit-fast data transfer into a snail. And how you can unlock the maximum potential of achieving High-res display, charging, and streaming simultaneously.
Not only that, you'll get to know the difference between USB4 and Thunderbolt 4, highlighting the importance of not overlooking manufacturer specifications. Rest assured, your time spent here will be worthwhile.
Disclaimer: In modern times, Dock and Hub do similar tasks; I've used the terms interchangeably.
USB-C accessories you can't ignore

🔵 Difference Between USB-C and Thunderbolt: A Recap of USB Technology
I don't want you to leave me here alone just to know about the USB versions (as I've mentioned them frequently) and their types. So, I went through some extra pain, explaining what was necessary.
🔹 Common Types of USB
▪️ USB 1.1 and 2.0
Regarding their data transfer speed, you can call them tortoises. USB 2.0 offers a maximum data transfer speed of 480Mbps (megabits per second).
▪️ USB 3.0, 3.1 and 3.2

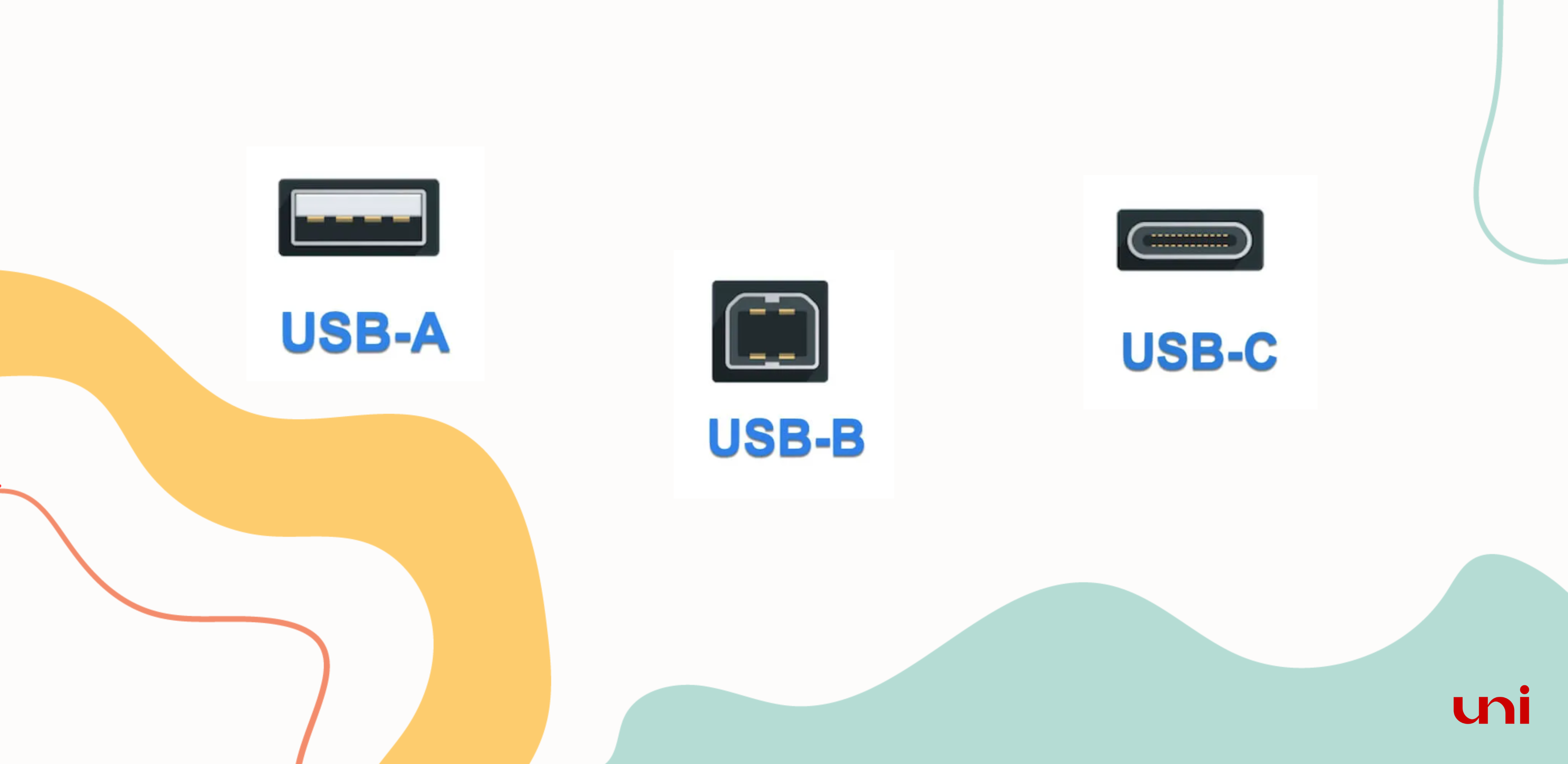
🔵 Connectors of USB
▪️ USB Type A - It's rectangular. You’ll find Type A in most computers, laptops, gaming consoles, and other peripheral devices.
▪️USB Type B - They're typically present in old printers and scanners.
▪️USB Type C - It's a game changer, killing other types of USB. With an oval-shaped reversible connector, you can plug it in either way. Type C supports high-speed data transfer, power delivery, and various protocols like USB 3.1, USB 3.2, Thunderbolt 3, DisplayPort, and more.
Till now, you've learned about USB (1.1, 2.2, 3.0, 3.1, 3.2, 4.0, 4.x) and their types. I wanted to take you directly to Thunderbolt and explain how it's different from USB-C, yet something more critical demands your attention.

🔵 Thunderbolt Vs. USB-C: Children of Different Parents
As we journey through the intriguing realm of technology, we encounter the formidable Godzilla-like presence of Thunderbolt, distinct from the Universal Serial Bus (USB) landscape. Thunderbolt and USB-C have distinct origins; the former was born from the collaboration between Apple and Intel, while the latter was birthed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF).
Do you know why Thunderbolt is roaring over other connectors regarding capability?
This is primarily due to its technological titans, Apple and Intel. Apple has always sought to outpace the competition - this principle has been fundamental to its survival and brand identity for nearly a decade. Today, Apple products are technically categorized as Intel-based Macs and Apple Silicon Macs. We'll talk about it later, PROMISE. Beyond their differing nomenclature, USB-C and Thunderbolt share many features.
Let's walk back to the topic.
So, to retain the status of Big Boss, Apple initiated full-scale research–in collaboration with Intel– to develop a protocol that could simultaneously carry power and video. Hence Thunderbolt was introduced in 2011 when USB-C was unforeseen. It was in 2014 when (after three years of Thunderbolt launch) USB-IF came out with USB-C.

[Image credit: AppleInsidder]
🔵 USB-C and Thunderbolt: Port Vs. Technology Explained
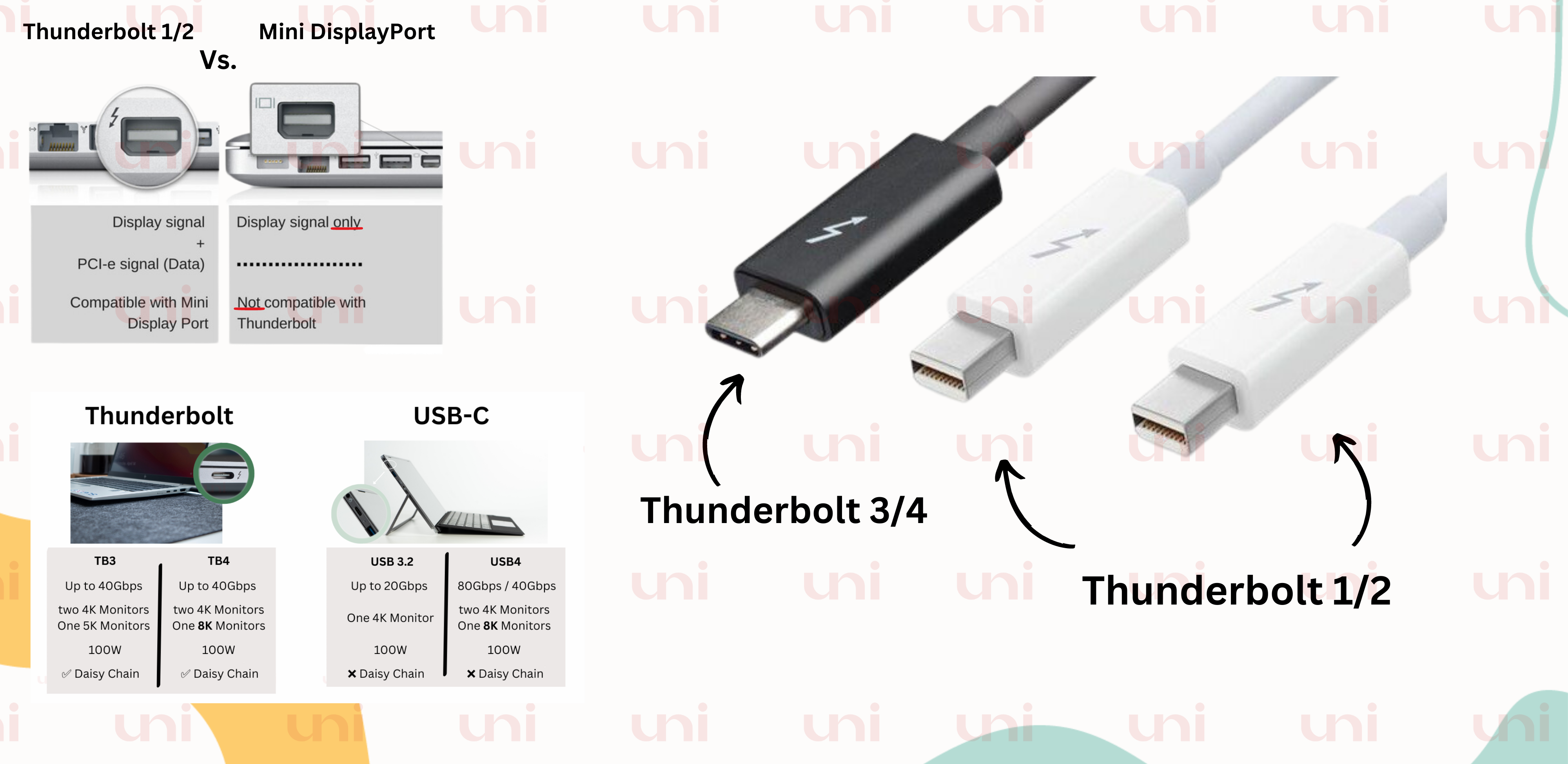
At first glance, a Thunderbolt 3/4 connector might appear identical to USB-C. However, Thunderbolt introduces advanced features such as daisy-chaining, data transfer rates up to 40 Gbps, and support for 5K displays. Much like USB, Thunderbolt has also progressed through several versions, currently at four.
A crucial distinction to note is that USB-C is a type of port, while Thunderbolt both refer technology and interface. Only USB-C ports equipped with USB 3.2 Gen 2 are compatible with Thunderbolt 3, and even then.
In some scenarios, the functionality may be limited.
When we say that a USB-C port compatible with Thunderbolt 3/4, it implies that the port is engineered with the requisite circuitry to manage Thunderbolt's high-speed data transfers and additional features.
🔵 What Is Thunderbolt 1 and 2?
🔵 What's Different In Thunderbolt 3?
The introduction of Thunderbolt 3 was not short of Tsunami. It shook the world, forcing the industry to adjust to emerging demand. Using a USB-C connector, Thunderbolt gets on board many devices, docks, and hubs. Having a bidirectional data transfer speed of 40 Gbps, Thunderbolt 3 allows for friendly communication with devices.
Not only that, Thunderbolt 3 backward compatibility with USB-C devices and acceptance of various protocols, including USB, DP, and PCle, created its space faster than expected.
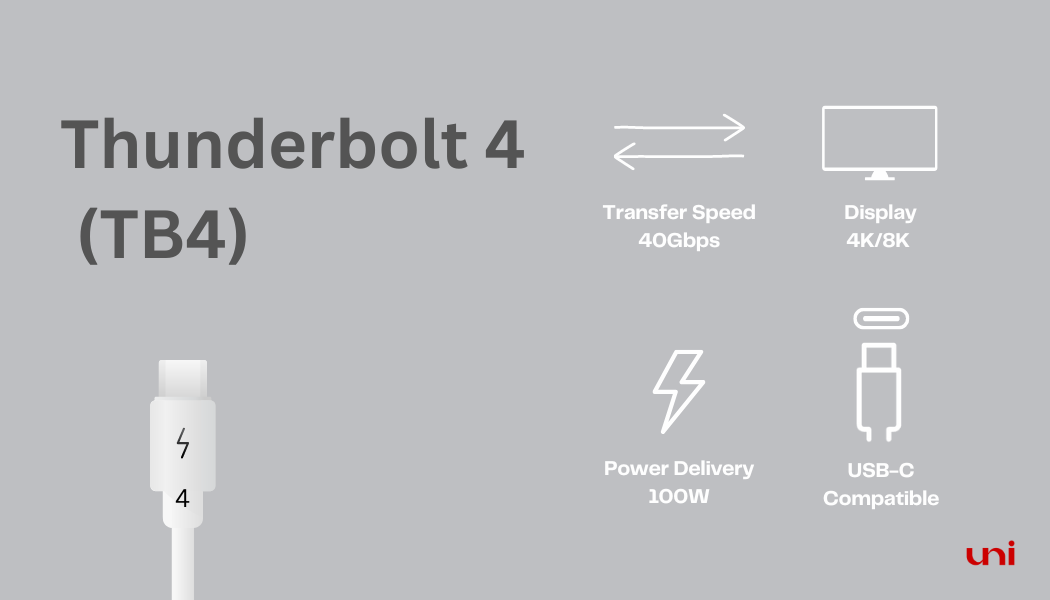
🔵 What Makes Thunderbolt 4 (TB4) Unique?
· It provides lightning-fast bidirectional bandwidth of 40 Gbps.
Imagine resting on your lounge's comfy seat. You crave to hear Miley Cyrus's captivating song, Flowers. You click play, and Thunderbolt opens a black hole of digital space, sucking the song in all its purity, soft vocals, and Miley's mild body movements in the blink of an eye.
· Thunderbolt 4 is backward compatible.
What does it mean for you? Imagine you plan to run nostalgia among family by showing old-family pictures saved in your Thunderbolt 3 external hard drive. Now you want to play on your TB4-enabled laptop. You get horrified thinking Will it work? Here Tb4’s backward compatibility will help you in bringing laughter. Similarly, you can seamlessly harness the features of HDMI, DP, and PCle.
· Power Delivery (100W).
Indeed, charging with100W TB4 power delivery is a true blessing for travelers, vloggers, and creators. It allows them to maximize their productivity and creativity by making the most out of limited time brackets when an electric socket is available.
· 4K or 8K Visual (Close to Human Eye Experience).
It supports connecting up to two 4K displays or one 8K display, enabling multi-monitor setups for enhanced productivity. You'll benefit if you’re a coder, a data analyst, or a video editor. Using multiple screens, you can connect a Tb4-enabled computer with two external monitors to easy complex coding, refined data analysis, and perfect image grading.
· Security (Stops Data Stealing)
Thunderbolt 4 incorporates advanced security features, including VT-d-based DMA protection, to safeguard against potential threats.
So far, we've learned about the specifications of USB in general and USB-C in particular. Here on, you'll learn about USB-C hubs and Thunderbolt docks.
In conclusion, you've as many ports and standards as you want. By the time you're reading, some manufacturers plan to delete ports further from laptops. They want to cut down expenses and shift the cost on Y.O.U. Port-deficient laptops and devices need Thunderbolt or USB Hubs to reach their maximum potential.
⏺ What is the Difference Between USB-C Dock and Thunderbolt 3/4 Dock?
Despite our efforts to present a consolidated explanation, USB and Thunderbolt connectivity standards can be as elusive as sand slipping through your fingers. Here, we delve into the primary characteristics and capabilities of Thunderbolt 3 and USB-C docks (with emphasis on USB 3.2 hubs).
While USB-C docks are beneficial, they do present some restrictions when interfacing with Thunderbolt:
-
Data Transfer Speed: USB-C might reduce the rapid data transfer speed typical of Thunderbolt.
-
Display Output: USB-C docks might struggle to support multiple displays or to match the display performance of Thunderbolt docks. Interestingly, you're more likely to find a DisplayPort in Thunderbolt docks than in USB-C hubs.
-
Power Delivery: USB-C docks often have a restrained power delivery capacity, which can affect their ability to charge certain devices or support high-performance tasks efficiently. But, with USB power delivery reaching up to 240W, this gap is set to narrow soon.
-
Peripheral Limitations: USB-C docks may not fully support all of Thunderbolt's unique peripherals, limiting their optimal use.

🔵 USB-C VS USB4 VS Thunderbolt 4 - Port VS Technology
Firstly, comparing USB-C (Type-C) with USB4 and Thunderbolt is like comparing apples with oranges. As noted earlier, USB-C is merely a connector type, while USB4 and Thunderbolt are technology. USB-C only facilitates these technologies to manifest their supremacy. In actual, you should look for a comparison between USB4 and Thunderbolt.
I've already enlightened you about the maximum data transfer speed of USB4 and Thunderbolt4, i.e., 40 Gbps. Now we are digging more. But, before we dive, I want to educate you about Minimum Link Speed.
Generally,"minimum link speed" refers to the lowest data transmission rate or speed a particular connection or interface can support. It represents the baseline speed you can expect from a device or cable.
▪️ If it's still confusing, read the next four sentences.
Suppose you are on a highway, allowing a maximum speed of up to 40km/s. On Saturday, you encounter heavy traffic with18-wheelers on the road unsuitable for such vehicles. These trucks are normally prohibited from using this route. Traffic density chocks the traffic flow. It reduces your car’s speed, but you still maintain 32 km/s of constant speed. As a result, you'll continue your journey at a reasonably fast speed.
Similarly, USB4 and Thunderbolt3 have a minimum link speed of 20 and 32 Gbps, respectively. Moreover, whereas a USB4 has a 7.5W minimum power requirement, Thunderbolt 4 doubles it to 15W. Regarding USB4, check the manufacturer's specs since they can choose between 20 and 40 Gbps. However, with Thunderbolt 4, you always get 32Gbps with 15W.
▪️ But do USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 always offers such high speeds?
Besides manufacturer's specs and device compatibility, another factor can damage data transfer speed. It's the size of a USB-C cable.
-
Thunderbolt is like a superhero, capable of maintaining blazing-fast 40Gbps speeds even when stretched over 2 meters.
-
USB4 is like sprinters with a limited range. They start strong but gradually lose their speed over longer distances. Once the cable reaches 2 meters or beyond, they settle for a still respectable 20Gbps.
◾️Honuring the Promise (Apple-Intel Partnership)
As promised, here is what intel-based and Apple Silicon Macs are:
Apple has seen two transitions in its manufacturing preferences. Before 2020, Apple collaborated with Intel and used its processors. Hence the Apple products launched until 2020 are technically called Intel-based Macs.
Since 2021 Apple has been regaining control over hardware and software used across its devices. It now uses chipped processors(M1 and M2), similar to those used in iPhones and iPads. As a result, apple launches beyond 2020 are known as Apple Silicon.
🔵 Difference Between USB-C and Thunderbolt: Final Words From Uni
In summary, comprehending the distinctions between Thunderbolt and USB-C is key to harnessing their full capabilities. Thunderbolt shines with its superior features and swifter data transfer speeds, while USB-C boasts broader adoption and can interface with Thunderbolt devices.
With the debut of USB4 and Thunderbolt 4, their prowess has further amplified. Both USB-C docks and Thunderbolt hubs are indispensable tools that widen our device's connectivity horizons. Still, they come with certain caveats, from data transfer rates and display outputs to power delivery and peripheral compatibility. As the tech landscape morphs, it's crucial to keep abreast of the evolving specs and standards of these ports.
So, which port will you choose to unlock the full potential of your devices?
People Also Read
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.
Also in Blog
How to Distinguish Low-Quality Electronic Waste on E-Commerce Platforms in 2025
March 19, 2025 3 min read
With the rise of online shopping, distinguishing between high-quality electronics and low-quality e-waste has become a critical skill. Many e-commerce platforms are flooded with questionable products that look appealing but often have serious quality and longevity issues.

Maximizing Your Internet Speed: The Ultimate Guide to Using a USB-C to Ethernet Adapter
July 12, 2024 4 min read
Read More Related Products
Recent Articles
- How to Distinguish Low-Quality Electronic Waste on E-Commerce Platforms in 2025 March 19, 2025
- Maximizing Your Internet Speed: The Ultimate Guide to Using a USB-C to Ethernet Adapter July 12, 2024
- How to Identify if a Device Supports UHS-II or UHS-I Protocols? June 24, 2024
- How to Use a USB-C Hub? Everything You Need to Know May 28, 2024
- Do I need a type c hub? What do you need to know before buying? April 12, 2024
- Can I Get 4k With USB-C to HDMI Cable or Hub? January 15, 2024
- Which USB-C Hub Should You Get? (Checklist) January 08, 2024
- Does USB-C Over Ethernet Work To Get Speedier Internet? January 01, 2024
- DisplayPort Over USB Type-C: The DP Alt Mode in Working December 27, 2023
- How to make Android phone Charge Faster (technician advice) December 11, 2023


